Gradle


Please feel free to contact us
Go
Gradle is an open-source build automation tool focused on flexibility and performance. Gradle build scripts are written using a Groovy or Kotlin DSL. Gradle is a powerful open-source build automation tool used primarily for Java projects but also supports other programming languages like Kotlin, Groovy, Scala, and C/C++. It provides a flexible and efficient way to automate the process of compiling, testing, packaging, and deploying software applications. Gradle is known for its speed, flexibility, and scalability, making it a popular choice for large-scale and complex software projects.
You can subscribe to this product from GCP Marketplace and launch an instance from the product’s image using the GCP compute service.
Note: The list of zones is randomized within each region to encourage use across multiple zones.
Create a boot disk no larger than 2 TB to account for the limitations of MBR partitions.
The GCP Console adds a network tag to your instance and creates the corresponding ingress firewall rule that allows all incoming traffic on tcp:80 (HTTP) or tcp:443 (HTTPS). The network tag associates the firewall rule with the instance. For more information, see Firewall Rules Overview in the Virtual Private Cloud documentation.
Step1: Do SSH to the virtual machine
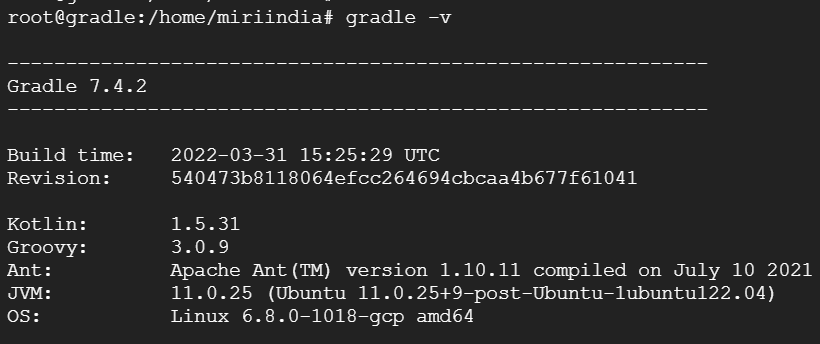
Step 2: Use the following Linux command to check Gradle installed successfully.
sudo su
and
gradle -v
All your queries are important to us. Please feel free to connect.
24X7 support provided for all the customers.
We are happy to help you.
Submit your Query: https://miritech.com/contact-us/
Contact Numbers:
Contact E-mail:
Until now, small developers did not have the capital to acquire massive compute resources and ensure they had the capacity they needed to handle unexpected spikes in load. Amazon EC2 enables any developer to leverage Amazon’s own benefits of massive scale with no up-front investment or performance compromises. Developers are now free to innovate knowing that no matter how successful their businesses become, it will be inexpensive and simple to ensure they have the compute capacity they need to meet their business requirements.
The “Elastic” nature of the service allows developers to instantly scale to meet spikes in traffic or demand. When computing requirements unexpectedly change (up or down), Amazon EC2 can instantly respond, meaning that developers have the ability to control how many resources are in use at any given point in time. In contrast, traditional hosting services generally provide a fixed number of resources for a fixed amount of time, meaning that users have a limited ability to easily respond when their usage is rapidly changing, unpredictable, or is known to experience large peaks at various intervals.
No. You do not need an Elastic IP address for all your instances. By default, every instance comes with a private IP address and an internet routable public IP address. The private address is associated exclusively with the instance and is only returned to Amazon EC2 when the instance is stopped or terminated. The public address is associated exclusively with the instance until it is stopped, terminated or replaced with an Elastic IP address. These IP addresses should be adequate for many applications where you do not need a long lived internet routable end point. Compute clusters, web crawling, and backend services are all examples of applications that typically do not require Elastic IP addresses.
Amazon S3 provides a simple web service interface that you can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web. Using this web service, you can easily build applications that make use of Internet storage. Since Amazon S3 is highly scalable and you only pay for what you use, you can start small and grow your application as you wish, with no compromise on performance or reliability.
Amazon S3 is also designed to be highly flexible. Store any type and amount of data that you want; read the same piece of data a million times or only for emergency disaster recovery; build a simple FTP application, or a sophisticated web application such as the Amazon.com retail web site. Amazon S3 frees developers to focus on innovation instead of figuring out how to store their data
Amazon RDS manages the work involved in setting up a relational database: from provisioning the infrastructure capacity you request to installing the database software. Once your database is up and running, Amazon RDS automates common administrative tasks such as performing backups and patching the software that powers your database. With optional Multi-AZ deployments, Amazon RDS also manages synchronous data replication across Availability Zones with automatic failover.
Since Amazon RDS provides native database access, you interact with the relational database software as you normally would. This means you’re still responsible for managing the database settings that are specific to your application. You’ll need to build the relational schema that best fits your use case and are responsible for any performance tuning to optimize your database for your application’s workflow.
Amazon S3 is secure by default. Upon creation, only the resource owners have access to Amazon S3 resources they create. Amazon S3 supports user authentication to control access to data. You can use access control mechanisms such as bucket policies and Access Control Lists (ACLs) to selectively grant permissions to users and groups of users. The Amazon S3 console highlights your publicly accessible buckets, indicates the source of public accessibility, and also warns you if changes to your bucket policies or bucket ACLs would make your bucket publicly accessible.
You can securely upload/download your data to Amazon S3 via SSL endpoints using the HTTPS protocol. If you need extra security you can use the Server-Side Encryption (SSE) option to encrypt data stored at rest. You can configure your Amazon S3 buckets to automatically encrypt objects before storing them if the incoming storage requests do not have any encryption information. Alternatively, you can use your own encryption libraries to encrypt data before storing it in Amazon S3.
Highly customisable — Gradle is modelled in a way that is customizable and extensible in the most fundamental ways.
Fast — Gradle completes tasks quickly by reusing outputs from previous executions, processing only inputs that changed, and executing tasks in parallel.
Powerful — Gradle is the official build tool for Android and comes with support for many popular languages and technologies.
 java
java