LEMP


Please feel free to contact us
Go
The LEMP stack is a popular open-source web server configuration that includes Linux, Nginx, MySQL (or MariaDB), and PHP. This stack is widely used for hosting dynamic websites and web applications due to its flexibility, performance, and reliability. Here’s a breakdown of each component in the LEMP stack:
You can subscribe to LEMP, an AWS Marketplace product and launch an instance from the product’s AMI using the Amazon EC2 launch wizard.
Step 1: SSH into Your Instance: Use the SSH command with the username ubuntu and the appropriate key pair to start the application.
Username: ubuntu
ssh -i path/to/ssh_key.pem ubuntu@instance-IP
Replace path/to/ssh_key.pem with the path to your SSH key file and instance-IP with your instance’s public IP address.
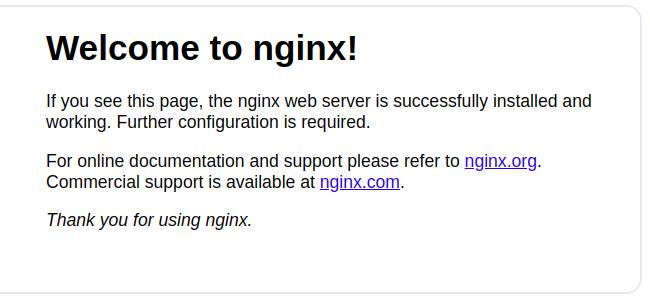
Step 2: Now, open your web browser and access Nginx web interface using the URL
http://instance-ip
All your queries are important to us. Please feel free to connect.
24X7 support provided for all the customers.
We are happy to help you.
Submit your Query: https://miritech.com/contact-us/
Contact Numbers:
Contact E-mail:
Amazon EC2 allows you to set up and configure everything about your instances from your operating system up to your applications. An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is simply a packaged-up environment that includes all the necessary bits to set up and boot your instance. Your AMIs are your unit of deployment. You might have just one AMI or you might compose your system out of several building block AMIs (e.g., webservers, appservers, and databases). Amazon EC2 provides a number of tools to make creating an AMI easy. Once you create a custom AMI, you will need to bundle it. If you are bundling an image with a root device backed by Amazon EBS, you can simply use the bundle command in the AWS Management Console. If you are bundling an image with a boot partition on the instance store, then you will need to use the AMI Tools to upload it to Amazon S3. Amazon EC2 uses Amazon EBS and Amazon S3 to provide reliable, scalable storage of your AMIs so that we can boot them when you ask us to do so.
Or, if you want, you don’t have to set up your own AMI from scratch. You can choose from a number of globally available AMIs that provide useful instances. For example, if you just want a simple Linux server, you can choose one of the standard Linux distribution AMIs.
Traditional hosting services generally provide a pre-configured resource for a fixed amount of time and at a predetermined cost. Amazon EC2 differs fundamentally in the flexibility, control and significant cost savings it offers developers, allowing them to treat Amazon EC2 as their own personal data center with the benefit of Amazon.com’s robust infrastructure.
When computing requirements unexpectedly change (up or down), Amazon EC2 can instantly respond, meaning that developers have the ability to control how many resources are in use at any given point in time. In contrast, traditional hosting services generally provide a fixed number of resources for a fixed amount of time, meaning that users have a limited ability to easily respond when their usage is rapidly changing, unpredictable, or is known to experience large peaks at various intervals.
Secondly, many hosting services don’t provide full control over the compute resources being provided. Using Amazon EC2, developers can choose not only to initiate or shut down instances at any time, they can completely customize the configuration of their instances to suit their needs – and change it at any time. Most hosting services cater more towards groups of users with similar system requirements, and so offer limited ability to change these.
Finally, with Amazon EC2 developers enjoy the benefit of paying only for their actual resource consumption – and at very low rates. Most hosting services require users to pay a fixed, up-front fee irrespective of their actual computing power used, and so users risk overbuying resources to compensate for the inability to quickly scale up resources within a short time frame.
No. You do not need an Elastic IP address for all your instances. By default, every instance comes with a private IP address and an internet routable public IP address. The private address is associated exclusively with the instance and is only returned to Amazon EC2 when the instance is stopped or terminated. The public address is associated exclusively with the instance until it is stopped, terminated or replaced with an Elastic IP address. These IP addresses should be adequate for many applications where you do not need a long lived internet routable end point. Compute clusters, web crawling, and backend services are all examples of applications that typically do not require Elastic IP addresses.
You have complete control over the visibility of your systems. The Amazon EC2 security systems allow you to place your running instances into arbitrary groups of your choice. Using the web services interface, you can then specify which groups may communicate with which other groups, and also which IP subnets on the Internet may talk to which groups. This allows you to control access to your instances in our highly dynamic environment. Of course, you should also secure your instance as you would any other server.
Running content management systems CMS like WordPress.
Hosting dynamic websites and web applications that require data handling.
Suitable for both small and large-scale deployments due to its flexibility and efficiency.
 LEMP
LEMP  php
php  nginx
nginx  mysql
mysql  linux
linux