OwnCloud


Please feel free to contact us
Go
OwnCloud develops and provides open-source software for content collaboration, allowing teams to easily share and work on files seamlessly regardless of device or location.
OwnCloud is an open-source software platform that provides file synchronization and sharing services. It allows users to store and manage their files on their own servers, offering a secure and private alternative to cloud services like Dropbox or Google Drive. Here’s a breakdown of its key features, benefits, and use cases:
You can subscribe to ownCloud, an AWS Marketplace product and launch an instance from the ownCloud product’s AMI using the Amazon EC2 launch wizard.
Step 1: SSH into Your Instance: Use the SSH command with the username ubuntu and the appropriate key pair to start the application.
Username: ubuntu
ssh -i path/to/ssh_key.pem ubuntu@instance-IP
Replace path/to/ssh_key.pem with the path to your SSH key file and instance-IP with the public IP address of your instance.
Step 2: Navigate to http://instance-ip. Enter all the details required to install the ownCLoud application.
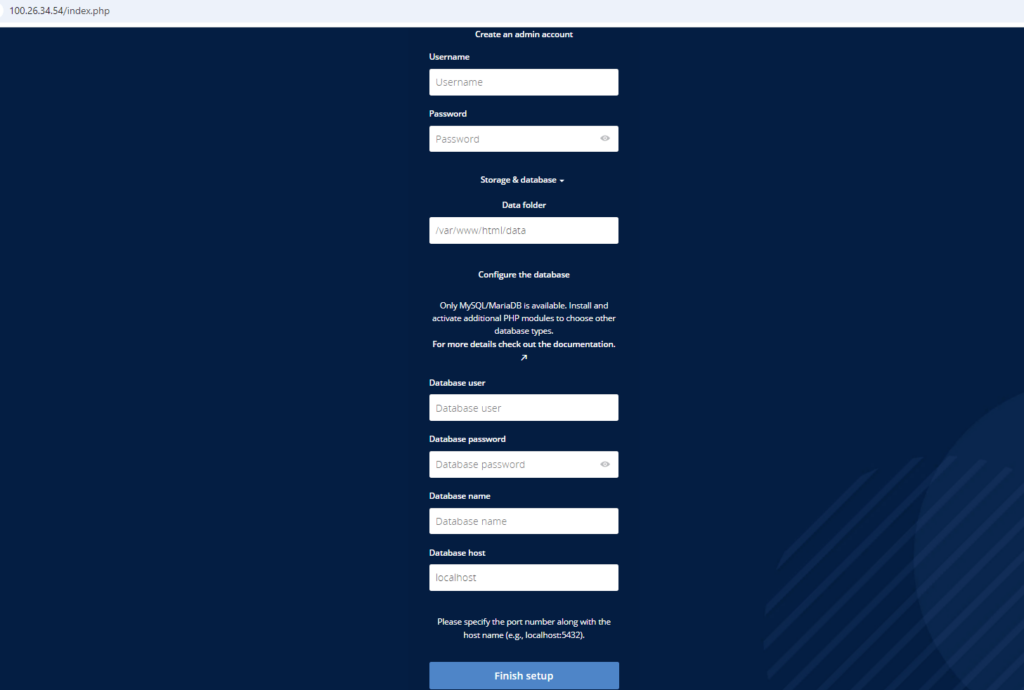
Database User: admin
Database Name: owncloud
Database password: Admin@123
Database Host: localhost
Click on the Finish Setup button to successfully install the application. Thank you.
All your queries are important to us. Please feel free to connect.
24X7 support provided for all the customers.
We are happy to help you.
Submit your Query: https://miritech.com/contact-us/
Contact Numbers:
Contact E-mail:
Amazon EC2 allows you to set up and configure everything about your instances from your operating system up to your applications. An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is simply a packaged-up environment that includes all the necessary bits to set up and boot your instance. Your AMIs are your unit of deployment. You might have just one AMI or you might compose your system out of several building block AMIs (e.g., webservers, appservers, and databases). Amazon EC2 provides a number of tools to make creating an AMI easy. Once you create a custom AMI, you will need to bundle it. If you are bundling an image with a root device backed by Amazon EBS, you can simply use the bundle command in the AWS Management Console. If you are bundling an image with a boot partition on the instance store, then you will need to use the AMI Tools to upload it to Amazon S3. Amazon EC2 uses Amazon EBS and Amazon S3 to provide reliable, scalable storage of your AMIs so that we can boot them when you ask us to do so.
Or, if you want, you don’t have to set up your own AMI from scratch. You can choose from a number of globally available AMIs that provide useful instances. For example, if you just want a simple Linux server, you can choose one of the standard Linux distribution AMIs.
You may connect your VPC to:
You have complete control over the visibility of your systems. The Amazon EC2 security systems allow you to place your running instances into arbitrary groups of your choice. Using the web services interface, you can then specify which groups may communicate with which other groups, and also which IP subnets on the Internet may talk to which groups. This allows you to control access to your instances in our highly dynamic environment. Of course, you should also secure your instance as you would any other server.
Amazon S3 provides a simple web service interface that you can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web. Using this web service, you can easily build applications that make use of Internet storage. Since Amazon S3 is highly scalable and you only pay for what you use, you can start small and grow your application as you wish, with no compromise on performance or reliability.
Amazon S3 is also designed to be highly flexible. Store any type and amount of data that you want; read the same piece of data a million times or only for emergency disaster recovery; build a simple FTP application, or a sophisticated web application such as the Amazon.com retail web site. Amazon S3 frees developers to focus on innovation instead of figuring out how to store their data
Amazon RDS manages the work involved in setting up a relational database: from provisioning the infrastructure capacity you request to installing the database software. Once your database is up and running, Amazon RDS automates common administrative tasks such as performing backups and patching the software that powers your database. With optional Multi-AZ deployments, Amazon RDS also manages synchronous data replication across Availability Zones with automatic failover.
Since Amazon RDS provides native database access, you interact with the relational database software as you normally would. This means you’re still responsible for managing the database settings that are specific to your application. You’ll need to build the relational schema that best fits your use case and are responsible for any performance tuning to optimize your database for your application’s workflow.
Amazon S3 is secure by default. Upon creation, only the resource owners have access to Amazon S3 resources they create. Amazon S3 supports user authentication to control access to data. You can use access control mechanisms such as bucket policies and Access Control Lists (ACLs) to selectively grant permissions to users and groups of users. The Amazon S3 console highlights your publicly accessible buckets, indicates the source of public accessibility, and also warns you if changes to your bucket policies or bucket ACLs would make your bucket publicly accessible.
You can securely upload/download your data to Amazon S3 via SSL endpoints using the HTTPS protocol. If you need extra security you can use the Server-Side Encryption (SSE) option to encrypt data stored at rest. You can configure your Amazon S3 buckets to automatically encrypt objects before storing them if the incoming storage requests do not have any encryption information. Alternatively, you can use your own encryption libraries to encrypt data before storing it in Amazon S3.
Control and Privacy
Customizability
Cost-Effective
Spaces
Secure by Design
 ownCloud
ownCloud  php
php  apache
apache  mysql
mysql  linux
linux